PREPARATION OF ALKANES
Alkanes can be prepared by various ways. General methods of preparation of alkanes are--
(1) From Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
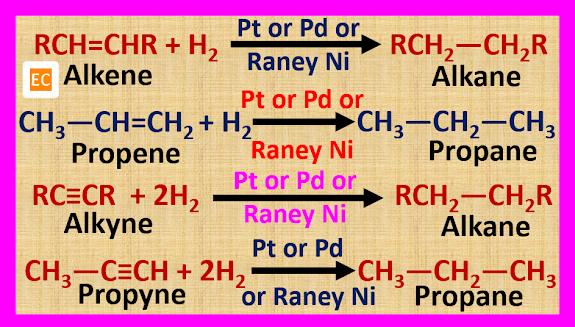
Alkanes are prepared by the catalytic reduction of unsaturated hydrocarbons such as alkene or alkyne in the presence of a suitable catalyst such as Ni, Pt, Pd, Raney Ni etc. Here hydrogen is added to an unsaturated hydrocarbon (alkene or alkyne) in the presence of a catalyst. This process is known as hydrogenation.
The catalytic hydrogenation reaction takes place at normal temperature and pressure if we use Raney Ni, Pt or Pd as a catalyst.
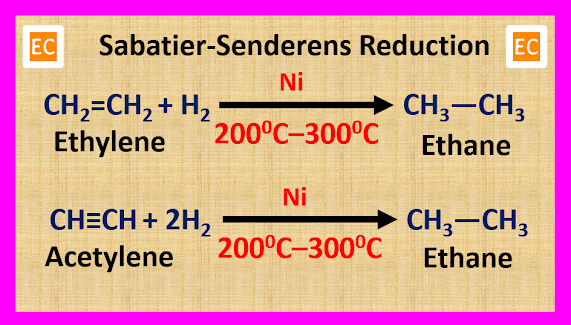
But if we use Ni as a catalyst, then the catalytic hydrogenation reaction takes place at 200 0C – 300 0C. The catalytic hydrogenation reaction in presence of a Ni catalyst at 200 0C – 300 0C is known as Sabatier-Senderens reduction.
(2) From Alkyl Halides
Alkanes can be prepared from alkyl halides in different ways---
(A) Through Grignard Reagent
When alkyl halide heated with magnesium powder in ether solution, alkyl magnesium halide (R―Mg―X) is produced. This alkyl magnesium halide (R―Mg―X) is known as Grignard reagent.
R―X + Mg → R―Mg―X
C2H5―I + Mg → C2H5―Mg―I
When Grignard reagent treated with water or dilute acid, alkane is produced.
R―Mg―X + H2O → RH + Mg(OH)X
C2H5―Mg―I + H2O → C2H6 + Mg(OH)I
(B) By Wurtz Reaction
In dry ether solution at normal temperature the reaction of two molecules of alkyl halide (preferably the bromide or iodide) with two molecules of pure and dry metallic sodium produce alkane.
R1―X + 2Na + R2―X → R1―R2 + 2NaX
CH3―Br + 2Na + CH3―Br → CH3―CH3
+ 2NaBr
If we use two types of alkyl halide, then mixture of alkanes is produced. It is difficult to separate this mixture of alkanes, because their close boiling point.
CH3―Br + 2Na + C2H5―Br → CH3―CH3 + C2H5―C2H5 + CH3―C2H5 + 2NaBr
This Wurth reaction is very useful for the synthesis of symmetrical alkane.
(C) By Corey-House Synthesis
In dry ether solution at normal temperature the reaction of alkyl halide with pure and dry metallic lithium produced alkyl lithium.
RX + 2Li → RLi + LIX
C2H5I + 2Li → C2H5Li + LiI
Reaction of alkyl lithium (RLi) with cuprous iodide (CuI) produced lithium dialkyl cuprate (R2CuLi).
2RLi + CuI → R2CuLi + LiI
2C2H5Li + CuI → (C2H5)2CuLi + LiI
Reaction of lithium dialkyl cuprate (R2CuLi) with another molecule of alkyl halide produced alkane.
R2CuLi + R'X → R―R' + RCu +LiX
(C2H5)2CuLi + CH3I → C2H5―CH3 + C2H5Cu + LiI
R and R' may be same or different. R group may be primary, secondary or tertiary but R' group always primary.
This Corey-House reaction is very useful for the formation of both symmetrical and unsymmetrical alkane.
(D) Reduction of Alkyl Halides
(i) Alkane is prepared by the reduction of alkyl halide by Zn and HCl.
C2H5Cl + Zn + HCl → C2H6 + ZnCl2
(ii) Alkane is prepared by the reduction of alkyl halide by Zn and NaOH.
Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + 2[H]
R―X + 2[H] → R―H + HX
(iii) When alkyl halide is reduced by Zn-Cu couple in presence of alcohol alkane is produced.
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e
R―X + e → R∙ + X-
R∙ + e → R:-
R:- + C2H5OH → R―H + C2H5O-
(iv) When alkyl halide is reduced by LiAlH4, NaBH4 or Ph3SnH alkane is produced.
R―X + H- → R―H + X-
(v) When alkyl halide is reduced by H2 in presence of Pd-C or Raney Ni, alkane is produced.
R―X + H2 → R―H + HX
(vi) When alkyl iodide is reduced by hydroiodic acid (HI) and red phosphorus at 150 0C, alkane is produced.
C2H5―I + HI → C2H6 + I2
(3) From Carbonyl Compounds
Alkane can be prepared from carbonyl compounds such as aldehyde and ketone by Clemensen reduction process and Wolf-Kishner reduction process.
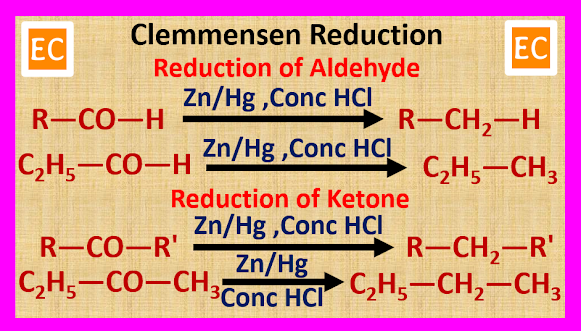
(A) By Clemmensen Reduction
When carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones are heated with zinc amalgam (Zn/Hg) and concentrated HCl, carbonyl compounds reduced to form alkane.
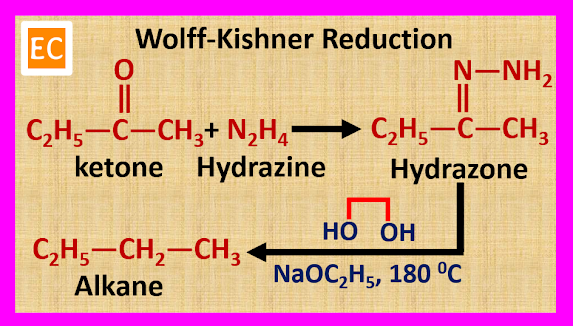
(B) By Wolff-Kishner Reduction
Carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine (H2N―NH2) to formed hydrazone. When the resulting hydrazone is heated with sodium ethoxide (NaOC2H5) and ethylene glycol (HOH2C―CH2OH) at 180 0C, alkane is produced.
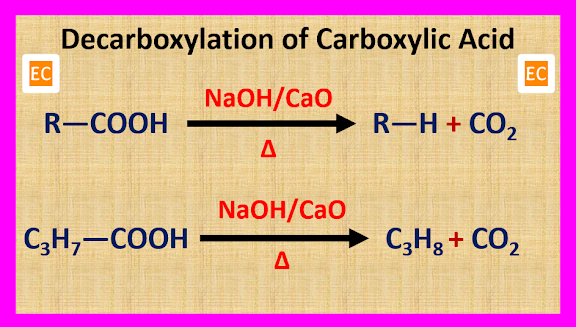
(4) From Carboxylic Acid
Alkane can be prepared from carboxylic acid by two methods. One is decarboxylation process and another is Kolbe’s electrolytic method.
(A) By Decarboxylation Process
Alkane is produced when carboxylic acid is heated with soda lime (NaOH + CaO). In this reaction CO2 is removed, so it is called decarboxylation reaction.
This is a degradation reaction, because in this process the number of carbon atom in the produced alkane is one less than that of the carboxylic acid.
(B) Kolbe’s Electrolytic Method
Electrolysis of a concentrated and cool aqueous solution of sodium or potassium salts of monocarboxylic acid using platinum electrodes produced alkane at the anode.
2R―COOK + 2H2O → [R―R + 2CO2(anode)] + [H2 + 2KOH (cathode)]
2CH3COOK + 2H2O → [C2H6 + 2CO2(anode)] + [H2 + 2KOH (cathode)]
Kolbe’s method of electrolysis is suitable for the preparation of even number of carbon atom alkane, but not suitable for the preparation of odd number of carbon atom alkane.
(5) From Alkyl Borane
Reaction of alkene with borane produced trialkyl borane.
3R―CH=CH2 + B2H6 → (R―CH2―CH2)3B
Alkane is produced by hydrolysis of the resulting trialkyl borane with acid.
(RCH2CH2)3B + 3CH3COOH → 3RCH2CH3 + (CH3COO)3B
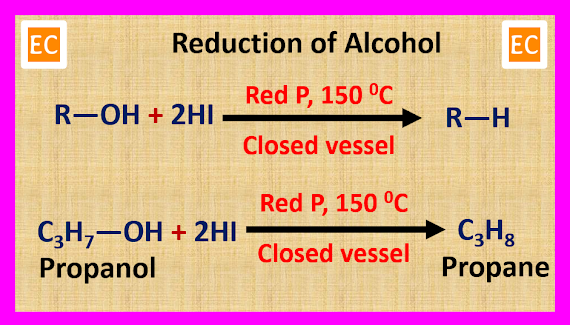
(6) From Alcohol
When alcohol is reduced by red phosphorus (P) and hydroiodic acid (HI) in a closed vessel at 150 0C, alkane is produced.











No comments:
Post a Comment