Polymers
The word polymers stands for many mers or parts. They are complex and giant molecules of high molecular weight (104
— 107). A polymer consists of a huge number of simple structural monomeric units which are repeated over and over again to form a giant molecule called a macromolecule. The simple unit is called the repeat unit. In the polymers -------X—X—X—X—X—X—X—X-------- and --------X—Y—X—Y—X—Y—X—Y—X—Y----------, for instance, the repeat units are
X and X—Y, respectively.
Example of polymers------
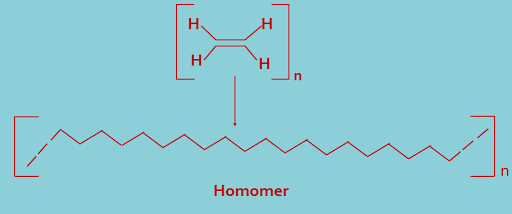
1. Polythene : Ethylene polymerizes to form polythene, here repeat unit is ethylene.
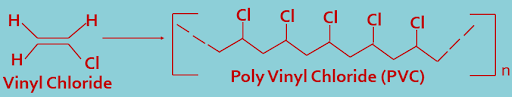
2. Polyvinyl Chloride : Vinyl chloride polymerizes to form polyvinyl chloride, here repeat unit is vinyl chloride.
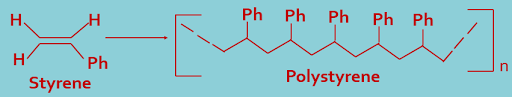
3. Polystyrene : Styrene polymerizes to form polystyrene. here repeat unit is styrene.
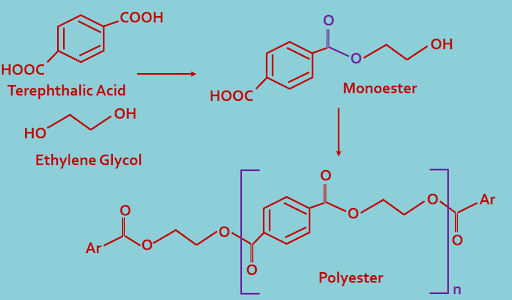
4. Polyester : Ester polymerizes to form polyester. Here repeat unit is ester.
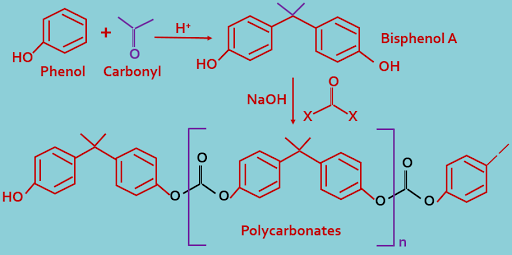
5. Polycarbonates : Phenol reacts with carbonyl compound to form bisphenol A, which reacts with again carbonyl compound in presence of base to form polycarbonates, here repeat unit is carbonyl substituted bisphenol A.
Classification of polymers
1.Classification based on the source of availability----
In this category of classification there are three types of polymers, such as polymers available from natural source, that are natural polymers, second type of polymers available from synthetic source, that are synthetic polymers, third type of polymers available from natural source but they are chemically or physically modified, that are semi-synthetic polymers.
(A). Natural polymers : This type of polymers available from natural source, such as animals and plants. Example of such polymers are starch, silk,wool, cellulose, natural rubber, proteins, nucleic acid, honey etc.
(B). Synthetic polymers : This type of polymers available from synthetic source, means they synthesized in chemical laboratory. Examples of such polymers are polythene, poly vinyl chloride, polystyrene, polyesters, polyamides, polycarbonates etc.
(C). Semi-synthetic polymers : This type of polymers obtained from natural source but they are chemically or physically modified. Examples of such polymers are rayon, cellulose nitrate, cellulose acetate etc.
2.Classification based on the type of monomers ------
(A). Homomer : In this type of classification polymers are made by only one type of monomer units. Examples are polythene made by ethylene monomer units, PVC made by vinyl chloride units etc.
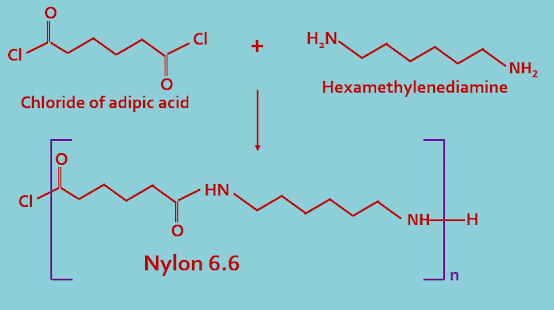
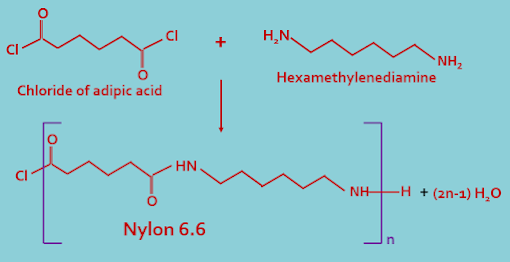
(B). Co-polymer : In this type of classification polymers are made by two or more types of monomeric units. Examples of such polymer is nylon 6.6.
3.Classification based on joining of monomer units----
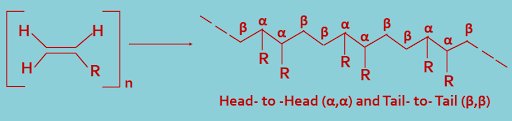
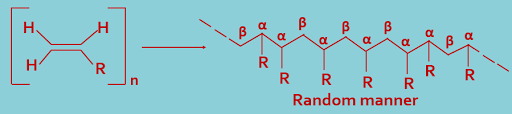
(A). Head-to-Head (α,α) or Tail-to-Tail (β,β) joining : During polymerization, the monomer molecules may combine in a head-to-head (α,α) or tail-to-tail (β,β) arrangement, as shown---
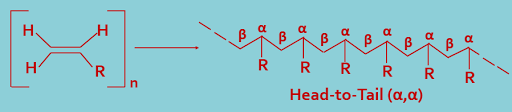
(B). Head-to-tail (α,β) joining : During polymerization, the monomer molecules may combine in a head-to-tail(α,β) arrangement,as shown---
(C). Random joining : During polymerization, the monomer molecules may combine in a random manner, as shown ----
4. Classification based on the structure of monomer chain----
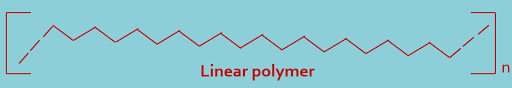
(A). Linear polymers : In this type of classification polymers containing long and straight chain, as shown---
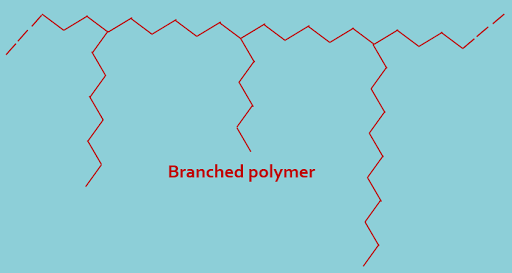
(B). Branched polymers : In this type of classification polymers containing chain that have several branches, as shown----
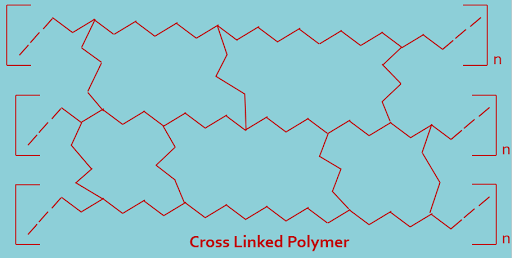
(C). Cross- Linked polymers : In this type of classification polymers are obtained when cross-link bond formed between monomeric units, as shown---
5. Classification based on configuration -----
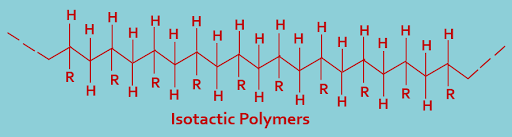
(A). Isotactic polymers : In this type of classification, polymers containing all the asymmetric carbon atoms have the same (d- or l-) configuration. The plane representation of an isotactic polymer is as shown below----
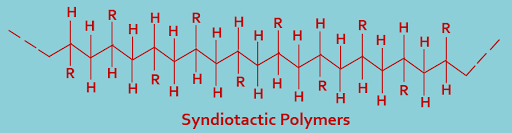
(B). Syndiotactic polymers : In this type of classification polymers having regular alternation of d- and l- configuration,that is substituent groups alternately lie above and below the main chain, as shown----
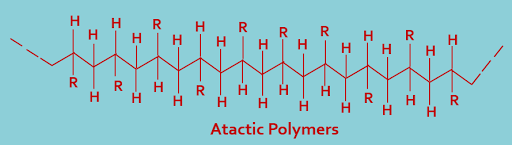
(C). Atactic polymers : In this type of classification polymers having random sequences of d- and l- configuration. The plane representation of an atactic polymer is as shown below----
Polymerization
In this process monomers are joined together, that is monomers units are repeated over and over again, to form large, chain like molecules. The process can be induced by heat and/or pressure or by using a catalyst, in the following two pathways such as ------
1. Addition or chain polymerization
2. Condensation or step polymerization.
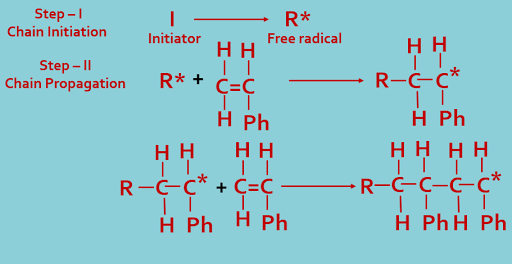
1. Addition or chain polymerization------
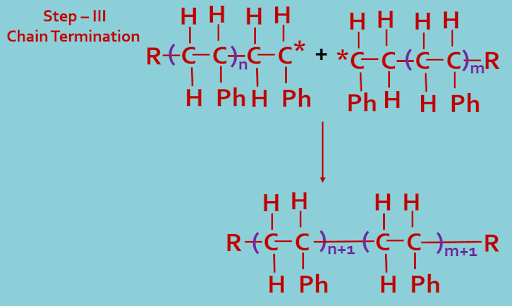
In this process small monomer units of one type or more types (two or more) joined together to formed long chain giant molecules by chemical reaction. The chemical reaction is initiated by means of a substance called initiator (I). The reaction process shown below---
2. Condensation or step polymerization-----
In this process of polymerization at least two bi or poly functional monomer units joined together to form a polymer by a chemical reaction with the production of a non polymerizable molecule such as water, CO, ammonia etc, reaction continues until almost all the monomeric reagent of one type used up.












No comments:
Post a Comment