Structure and Bonding of Diborane (B2H6)
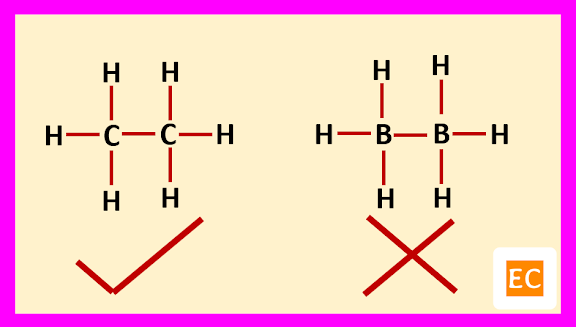
Boron is an electron deficient element. Due to its electron deficient character, the trivalent boron leads to dimerization to form diborane (B2H6). If we assumed that, the structure of diborane (B2H6) is similar to single bond structure of ethane (C2H6), then this assumption is rejected because single bond structure of ethane (C2H6) contains 14 electrons [(4+4 = 8 electrons from two carbon atoms) and (1x6 = 6 electrons from six hydrogen atoms)] but in diborane there are only 12 electrons [(3+3 = 6 electrons from two boron atoms) and (1x6 = 6 electrons from six hydrogen atoms)].
If we further assumed that, diborane (B2H6) molecule contains two one-electron bonds in its structure, to account for 12 electrons then diborane (B2H6) must be paramagnetic but actual fact that, the diborane (B2H6) molecule is diamagnetic. So, this assumption is also rejected.
Again, if we further assumed that, the diborane (B2H6) molecule contain two-electron three-centred bond (2e-3c bond), then the problem has been solved.
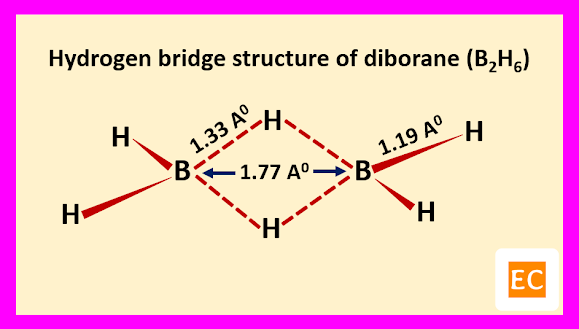
Electron diffraction study and other physical studies indicate the below structure for the molecule of diborane (B2H6).
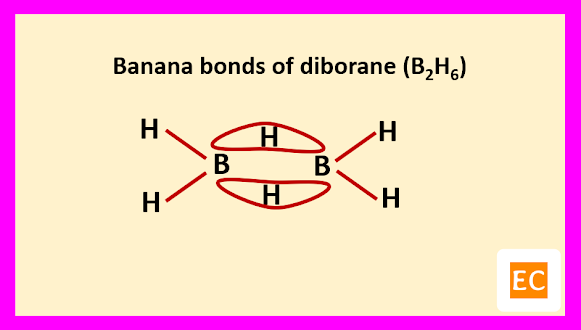
Two B―H―B bridges joined the two B atoms. The B―H bridge bond length (1.33 A0) are longer than B―H terminal bond length (1.19 A0). The B―B distance is 1.77 A0. Specific heat measurement data confirm that the two bridging H-atoms are in a plane perpendicular to the rest of the molecule and prevent rotation between the two B-atoms.
Raman spectroscopy confirm that four terminal H-atoms are in a different environment from two bridging H-atoms. It is also confirmed by the fact that, methylation of diborane (B2H6) with B(CH3)3 produced tetramethyl diborane [(CH3)4B2H2], further attempt for methylation breaking the molecule into B(CH3)3 fragments. Four terminal H-atoms which are linked to B-atoms by normal covalent bonds, means two-electron two-centred bond (2e-2c) are replaced on methylation. The two bridging H-atoms, which are not methylated are connected through peculiar two-electron three-centred (2e-3c) bonds. The whole structure of diborane (B2H6) molecule can be explained as follows.
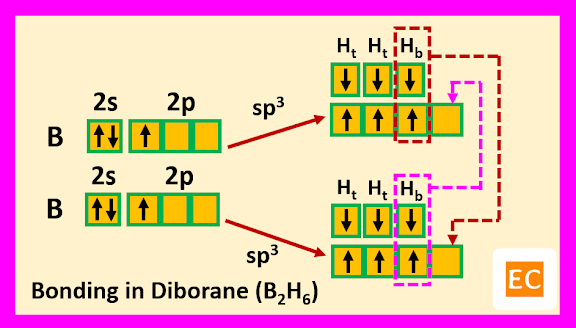
Electron configuration of boron is----
1s2 2s2 2p3
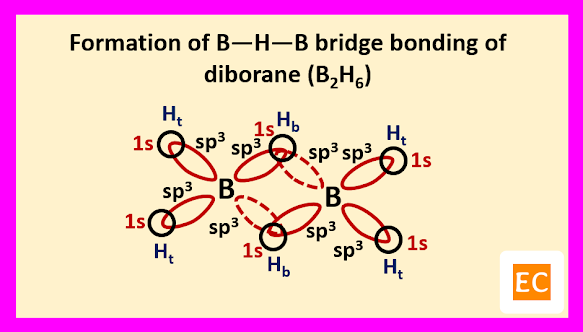
So, boron contains three electrons in its outermost shell. Two boron atoms of diborane (B2H6) molecule undergoes sp3 hybridisation. Two sp3 hybrid orbitals of each boron atoms overlap with the 1s orbitals of two terminal H-atoms.
The other two sp3 hybrid orbitals of one B atom overlap with two other sp3 hybrid orbitals of another B atom through the 1s orbitals of the two bridging H-atoms. As a result of these overlap, there formed total two B―H―B two-electron three-centred (2e-3c) bonds.
Such type of bond or molecular orbital has banana shape, so these bent bonds are called banana bonds.
Molecular orbital approach of diborane (B2H6) molecule---
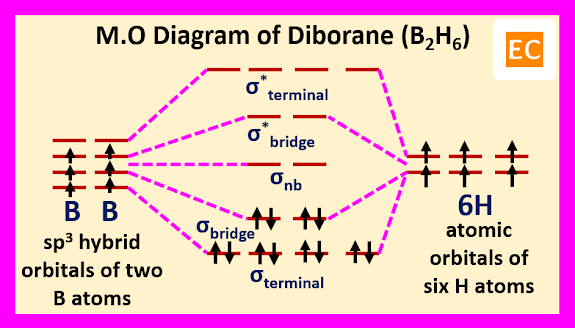
Molecular orbital approach of diborane molecule begin with four roughly sp3 hybrid orbitals of each boron atoms and the 1s atomic orbitals of six hydrogen atoms. Two sp3 hybrid orbitals of each boron overlap with two 1s atomic orbitals of two hydrogen atoms and formed four terminal B―H bonds (covalent bonds, 2e-2c bonds). Due to this overlap four bonding and four anti bonding molecular orbitals are formed by four sp3 hybrid orbitals of two boron (two sp3 hybrid orbitals of each boron) and four 1s atomic orbitals of four hydrogen atoms. The four bonding molecular orbitals are occupied by eight electrons (four electrons from two boron atoms and four electrons from four hydrogen atoms). Remaining four sp3 hybrid orbital of two boron (two sp3 hybrid orbitals from each boron) and two 1s atomic orbitals of remaining two hydrogen atoms forms two sets of B―H―B bridge bonds (2e-3c bonds). Due to this overlap three sets of molecular orbitals are formed. One set of bonding molecular orbitals, one set of nonbonding molecular orbitals and one set of antibonding molecular orbitals. Remaining four electrons (two from two boron atoms and two from two hydrogen atoms) occupied the lowest energy bonding molecular orbitals.











No comments:
Post a Comment