CONDUCTOMETRIC TITRATIONS
Conductometric titration of strong acid with strong base
Consider the conductometric titration of a strong acid, HCl with a strong base, NaOH. Since both the acid HCl and the base NaOH are strong, so complete dissociation occurred. Here neutralization mean replacement of H+ ions by an equal number of Na+ ions.
H+ + Cl- + [Na+ + OH-]
-----> Na+ + Cl- + H2O
H+ ion has much higher ionic conductance than that of Na+ ion. So, the conductance of the solution will decrease as more and more NaOH is added. When all the H+ ions replaced by the Na+ ions, conductance will reach the lowest limit. Any subsequent addition of NaOH means increase in the numbers of both Na+ ions and fast moving OH- ions. These are no longer removed, the conductance therefore increases linearly with addition of NaOH. On plotting the conductance against the volume of alkali added, the point of intersection of two lines, that is the lowest point, corresponds to the minimum conductance, which is the exact neutralization point of this conductometric titration between HCl and NaOH.
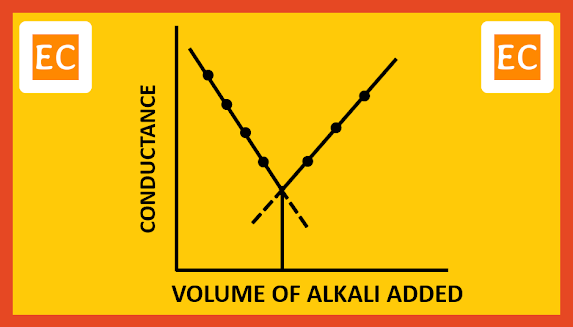 |
| Strong acid with strong base |
Conductometric titration of weak acid with strong base
Consider the conductometric titration of a weak acid, CH3COOH with a strong base NaOH. Since the acid is weak, the conductance of the acid will be low on account of its poor dissociation. As NaOH is added the OH- ion removed the H+ ion by producing H2O. Undissociated CH3COOH molecules produce fresh H+ ions. The conductivity of the solution rises due to presence of some Na+ ions. At the starting stage, due to common ion effect, there may be a little fall in conductivity, but later on this fall will be insignificant compared to rise in the conductivity of the solution due to the added new Na+ ions.
CH3COOH+[Na+ + OH-] ----> CH3COO- + Na+ + H2O
The total volume of CH3COOH dissociates slowly in this way and is neutralized. When the acid is completely neutralized, further addition of NaOH will increase the conductivity of the solution, because OH- ions have large ion-conductance. On plotting the conductance against the volume of alkali added, the point of intersection is obtained by extending the lines, which gives the end point.
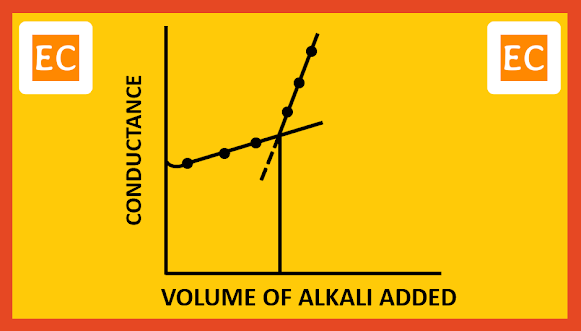 |
| Weak acid with strong base |
Conductometric titration of mixture of strong and weak acids with strong base
Suppose of a mixture of strong acid HCl and weak acid CH3COOH, is to be titrated with a strong base NaOH. Since HCl is much stronger acid than CH3COOH, HCl will get titrated first. When HCl is completely neutralized by NaOH, then titration of CH3COOH will start. On plotting the conductance against the volume of alkali added, the following type of curve is obtained.
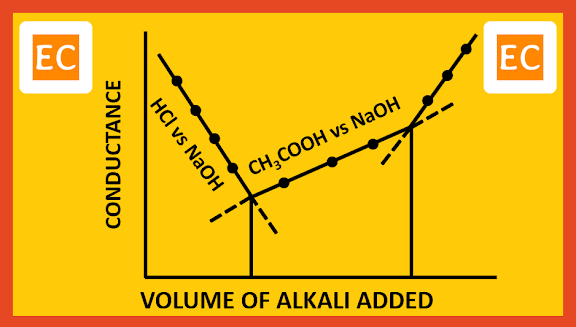 |
| Mixture of strong and weak acids with strong base |
Conductometric titration of strong acid with weak base
Consider the conductometric titration of a strong acid, HCl by a weak base, NH4OH. The conductance of the solution will decrease due to the replacement of fast-moving H+ ions by slow moving NH4+ ions. When all the H+ ions replaced by the NH4+ ions, conductance will reach the lowest limit and neutralization point comes.
H+ + Cl- + NH4OH -----> NH4+ + Cl- + H2O
Due to weakly ionized nature of NH4OH, further addition of NH4OH will not cause any appreciable change in the conductance. On plotting the conductance against the volume of alkali added, the following type of curve is obtained.
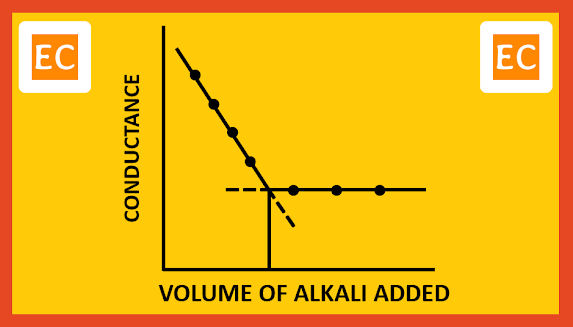 |
| Strong acid with weak base |
Conductometric titration of weak acid with weak base
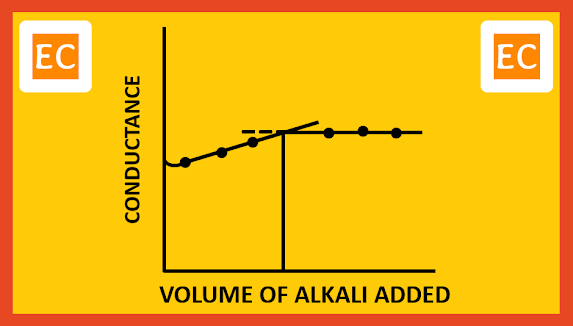
Consider the conductometric titration of a weak acid, CH3COOH by a weak base NH4OH. Since the acid is weak, the conductance of the acid will be low on account of its poor dissociation. As NH4OH is added, the OH- ions removed the H+ ions. Undissociated CH3COOH molecules produced fresh H+ ions. Besides the solution has some NH4+ ions. At the starting stage, due to common ion effect there may be little fall in conductivity. But later on, the conductivity of the solution increases slowly due to the presence of slow moving NH4+.
CH3COOH + NH4OH ----> CH3COO- + NH4+ + H2O
The total volume of CH3COOH dissociates slowly in this way and neutralized. Due to weakly ionized nature of NH4OH, further addition of NH4OH will not cause any appreciable change in the conductance. On plotting the conductance against the volume of alkali added, the following type of curve is obtained.
 |
| Weak acid with weak base |











No comments:
Post a Comment