The photosynthetic process in green plants consists of splitting the elements of water, followed by carbon dioxide:
2H2O ------> [4H] + O2
xCO2 + x/2[4H]------> (CH2O)x
+ x/2 O2
Where [4H] does not imply free atoms of hydrogen but a reducing capacity of four equivalents.
The overall reaction may be written as----
xCO2 + xH2O ------> (CH2O)x
+ xO2
All the dioxygen come from oxidation of H2O, as shown by the use of labelled H2O* (O* = 18O):
xCO2 + 2xH2O* -------> (CH2O)x
+ xO2* + xH2O
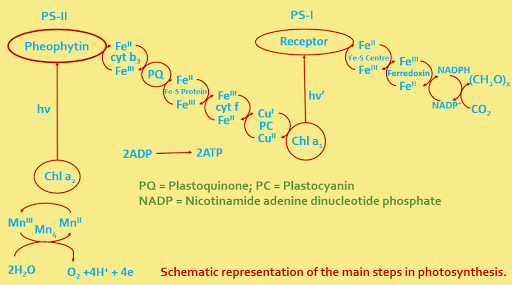
In all dioxygen-producing organism ranging from cyanobacteria to algae to higher plants, there are two coupled photosynthetic systems, PS I and PS II. The primary product of PS I is reduced carbon, and the primary product of PS II is energy in the form of two moles of ATP with molecular oxygen as a chemical by product.
The energy of an absorbed photon in either PS I or PS II initiates a series of redox reactions. System I produces a moderately strong reducing species (REDI) and a moderately strong oxidising species (OXI). System II provides a strong oxidising agent (OXII) but a weaker reducing agent (REDII).
For the production of molecular oxygen in photosynthesis responsible is OXII . A manganese complex, probably containing four atoms of manganese, is attached to a protein molecule. It reduces OXII which is recycled for use by another excited chlorophyll molecule in PS II. In the redox reactions the manganese shuttles between two oxidation states with each manganese atom increasing (and subsequently decreasing) its oxidation state by one unit. In the reduced form the oxidation states may be as low as three Mn(II) and one Mn (III), but they are more likely to be three Mn (III) and one Mn (IV).
The overall photosynthetic conversion is the outcome of a series of complex reactions and involves light absorption at two different regions of wave length, PS I having absorption maxima at 700 nm (P-700) and PS II having maxima at 680 nm (P-680).
Photosystem - II : A manganese clustuer (Mn4) catalyses the oxidation of water to dioxygen; the metalloenzyme is called oxygen -evolving complex (OEC):
2H2O -------> O2 + 4H+ +
4e
The electrons are excited photochemically by P-680 to the primary electron acceptor pheophytin. Therefore it is transferred to PS I via the intermediacy of (i) cytochrome b3 (ii) plastoquinone (iii) Rieske's Fe-S protein (iv) cytochrome f and (v) plastocyanin.
Photosystem - I : The electron received from PS II is further excited by P-700 and is ultimately used up in the reduction of CO2 via (i) an Fe-S center (ii) Ferredoxin NADP reductase and (iii) NADPH. The electron flow also results in the formation of ATP from ADP.
The main reactions may be summarily represented as ---

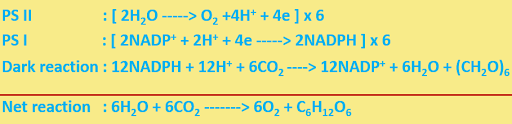










No comments:
Post a Comment