SILICONES
A group of organosilicon polymers containing linkages of the type (---O―Si―O---) are called silicones. Generally, silicones are three types, such as linear silicones, cyclic silicones and cross-linked silicones.
Preparation of Silicones
Silicones are prepared in three steps, such as preparation of alkyl or aryl chlorosilanes, hydrolysis of alkyl or aryl chlorosilanes to produced silanols and polymerization of silanols.
(1) At first, alkyl or aryl chlorosilanes are prepared by the following way---
(i) When alkyl or aryl chloride (R―Cl) are heated with silicon (Si) at 300 0C in presence of Cu catalyst, mixture of alkyl or aryl chlorosilanes are produced.
2R―Cl + Si ----> RSiCl3 + R2SiCl2 + R3SiCl
(ii) Reaction of Grignard reagent (R―MgCl) with SiCl4 produced alkyl or aryl chlorosilanes.
R―MgCl + SiCl4 ----> RSiCl3 + MgCl2
2R―MgCl + SiCl4 ----> R2SiCl2 + 2MgCl2
3R―MgCl + SiCl4 ----> R3SiCl + 3MgCl2
(2) Hydrolysis of alkyl or aryl chlorosilanes to produced silanols----
When alkyl or aryl chlorosilanes treated with water, silanols are produced.
RSiCl3 + 3H2O ----> RSi(OH)3 + 3HCl
R2SiCl2 + 2H2O ----> R2Si(OH)2 + 2HCl
R3SiCl + H2O ----> R3SiOH + HCl
(3) Polymerisation of Silanols---
In the polymerisation process some molecules of H2O are removed and form various types of silicones such as linear, cyclic or cross linked according to the nature of the alkyl or aryl hydroxy (silanols) derivatives----
(i) Linear silicones---
Polymerisation of dialkyl dihydroxy silane [R2Si(OH)2] gives rise to straight chain linear silicone polymers and as an active OH group is left at each end of the chain, polymerisation continues and the chain increases in length. Thus dialkyl dihydroxy silane [R2Si(OH)2] is a chain building unit. High polymers are obtained in this way. The structure of linear silicone polymer is as follows---
(ii) Cyclic silicones---
Careful polymerisation of dialkyl dihydroxy silane [R2Si(OH)2] can produced cyclic silicone structure containing three, four, five or six silicon (Si) atoms. The structure of cyclic silicone polymer is as follows--
(iii) Cross linked silicones---
Polymerisation of alkyl trihydroxy silane [RSi(OH)3] gives rise to cross linked two dimensional silicone polymers and as an active OH group is left at each end of the chain, polymerisation continues and chain increases in length. The structure of cross linked silicone polymer is as follows---
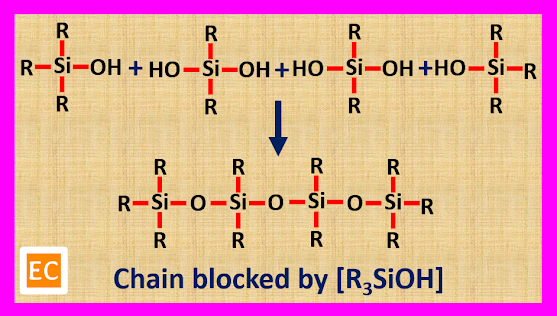
Polymerisation of trialkyl monohydroxy silane [R3SiOH] gives rise to linear straight chain silicone dimer. The structure of silicone dimer is as follows---
Trialkyl monohydroxy silane [R3SiOH] is used as a chain blocking unit. When some trialkyl monohydroxy silane [R3SiOH] is mixed with dialkyl dihydroxy silane [R2Si(OH)2], the trialkyl monohydroxy silane [R3SiOH] will block the chain produced by dialkyl dihydroxy silane [R2Si(OH)2].
Some Important Silicones
(1) High thermal silicones---
When hydrolysis of alkyl or aryl chlorosilanes is carried out in presence of aluminium halides, titanium halides, aluminium alkoxides or titanium alkoxides two dimensional linear or cyclic high thermal silicone polymer is obtained in which some silicon (Si) atoms are replaced by aluminium (Al) or titanium (Ti) atoms. The presence of Al or Ti atoms in the silicone polymer structure, increases the thermal stability of the polymer. This silicone polymer has exceptionally high thermal stability. The structure of high thermal silicone polymer is as follows---
(2) Silicone oil---
When some trialkyl monohydroxy silane [R3SiOH] is mixed with dialkyl dihydroxy silane [R2Si(OH)2], silicone oil is obtained. It has low temperature coefficient of viscosity, high thermal stability and good insulating properties. The structure of silicone oil is as follows---
(3) Silicone rubbers---
Silicone rubbers are long chain polymer, with some cross linking between the chains. These rubbers retain its elasticity and shape even after vulcanization.
Properties and Uses of Silicones
Silicones are thermally stable, chemically inert, excellent water repellent, good electrical insulator and non toxic. They are resistance to oxidation and most chemicals such as acids, alkalies etc due to their chemical inertness. Their inertness is due to their stable silica like skeleton and high strength of Si―C bonds. They have non stick properties.
They are used in making waterproof cloth, in lubrication, as insulating materials, as antifoams, in cosmetics, as stop cock grease, in electric motor and other electric appliances, as hydraulic fluids, as dielectric fluids etc.











No comments:
Post a Comment