Boron Nitride (Inorganic Graphite)
Much of B—N chemistry relates that a BN unit isoelectronic with the CC unit. The electronegativity and atomic radius of carbon are intermediate between boron and nitrogen. Therefore there are many azoborane analogues of hydrocarbon in which a pair of carbon atoms replace B and N unit. Boron Nitride an important ceramic material that is isoelectronic with graphite. Boron Nitride has a similar sheet-like structure except that rings are aligned in an eclipsed fashion rather than staggered in graphite. Hexagonal Boron Nitride is colourless, electrically nonconducting, and is more resistant to chemical attack than graphite.
Preparation of Boron Nitride
Boron reacts with N or NH3 on heating to form a binary nitride BN which is a white refractory solid. This compound is also obtained by fusing borax with NH4Cl.
Na2B4O5(OH)4 +
2NH4Cl -----> 2NaCl + 2BN + 2B2O3 + 6H2O
Pure Boron Nitride is best obtained by heating boron amide. This decomposes first to boron imide and finally into Boron Nitride.
2B(NH2)3 -----> B2(NH)3
+ 3NH3
B2(NH)3 ------> 2BN + NH3
Boron Nitride is also prepared by heating borazine--
B3N3H6 ------> 3BN + 3H2
Property of Boron Nitride
Boron Nitride is a white powder of density 2.34. It melts under pressure at 3000 0C. It is a high melting refractory solid, very stable, and unreactive. It is unchanged by aqueous acids or alkalis, Cl2, H2, O2, etc.
It is decomposed by steam --
It reacts with F2 and HF at a lower temperature --
2BN + 3F2 = 2BF3 + N2
BN + 4HF = NH4BF4
It is decomposed by alkali on fusion --
BN + KOH + H2O = KBO2 + NH3
Structure of Boron Nitride
One B atom and one N atom together have the same no of valence electron as two carbon atoms. Thus Boron Nitride has a graphite-like layer structure. The layers are made up of hexagonal rings of alternate B and N atoms joined together. The B—N distance (1.45 A) in Boron Nitride is comparable to the C—C distance (1.42 A) in graphite. The layer spacing in Boron Nitride and graphite is also comparable. Both have the same density. This form of Boron Nitride is often called Inorganic Graphite. Each B and N is sp2 hybridized as each six C-atom in graphite. The three sp2 hybrid orbitals of each B overlaps with hybrid orbitals of three neighboring N atoms. The unhybridized p-orbital then accepts a lone pair forming a π-bond. Through resonance, all the B—N bonds become equivalent in Boron Nitride.
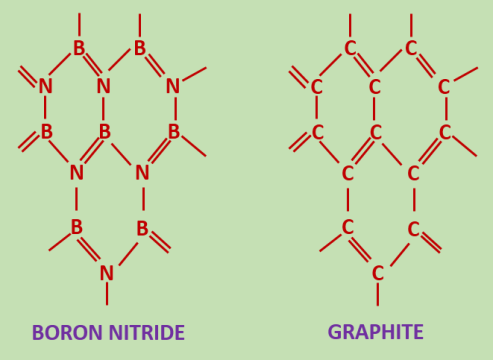 |
| Structure of Boron Nitride and Graphite |
Uses of Boron Nitride
Boron Nitride possesses the same hardness as diamond and can withstand a temperature of more than 3000 0C. Due to this property Boron Nitride is used for coating crucible linings, it is also used as a lubricant.












No comments:
Post a Comment