SUCROSE
STRUCTURE DETERMINATION
Sucrose exists in two crystalline forms, a stable form, sucrose A, m.p. 184 -185 0C, and the unstable form, sucrose B, m.p. 169 -170 0C. Sucrose has been shown to be α-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-fructofuranoside. Sucrose is hydrolysed by dilute acids or by the enzyme invertase to an equimolecular mixture of D (+)-glucose and D (-)-fructose. Methylation of sucrose gives octa-O-methylsucrose and this, on hydrolysis with dilute hydrochloric acid gives 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-methyl-D-glucose and 1,3,4,6-tetra-O-methyl-D-fructose. Thus glucose is present in the pyranose form, and fructose as the furanose.
Since sucrose is a non reducing sugar, both glucose and fructose must be linked via their respective reducing groups.
Sucrose is hydrolysed by the enzyme maltase, thus indicating the α-link is present. Again the glucose which is formed by hydrolysis of sucrose shows downward mutarotation. It therefore indicates that α-glucose is present in sucrose. There is an enzyme invertase which hydrolyzes methyl-β-fructofuranosides, and it has been found that it also hydrolyses sucrose. This suggest that fructose is present in sucrose in the β-form.
Oxidation of sucrose with periodic acid confirms its structure. Three molecules of periodic acids are consumed and one molecule of formic acid is produced. Consumption of three moles of HIO4 indicates presence of six membered ring of a monosaccharide and five membered ring of another in sucrose. Formation of one mole of HCOOH confirms, it is the glucose which is six membered and fructose which is five membered.
 |
| Structure of sucrose |
INVERSION OF SUCROSE
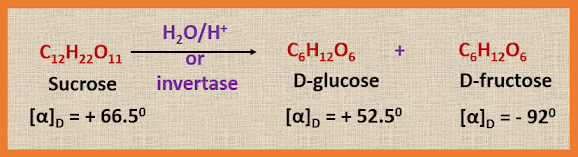
Hydrolysis of sucrose to D-glucose and fructose is very interesting in two ways. Firstly, the dextrorotatory sucrose gives the laevorotatory product on hydrolysis. The reason being the sucrose with [α]Dt
= + 66.50, on hydrolysis gives an equilibrium mixture of glucose, [α]Dt
= + 52.50 and fructose [α]Dt = - 920.
Now as the specific rotation value of fructose is high as compared to glucose as well as the parent compound sucrose, the mixture after hydrolysis will be, on the whole laevorotatory. Furthermore, since the direction of rotation is reversed (or inverted), the mixture of sugars formed on hydrolysis with a specific rotation of - 200 is
known as invert sugar. Thus invert sugar is the equimolecular mixture of D-glucose and D-fructose obtained on hydrolysis of sucrose.
 |
| Hydrolysis of sucrose |
The specific rotation of invert sugar is one half the sum of these of the individual monosaccharides:
1/2 [+ 52.50
+ (- 920)] = - 200
It is also interesting that the sucrose after hydrolysis is more sweeter than the sucrose itself. The reason being the presence of fructose in invert sugar which is the sweetest of all the sugars. This also explains why honey (containing a large proportion of invert sugar, that is formed by the hydrolysis of honey by the saliva of bees) is sweeter than sucrose. The relative sweetness of the common sugars as determined practically by taking the sucrose as an orbitary standard value of 100 are given below:
 |
| The relative sweetness of sugar |
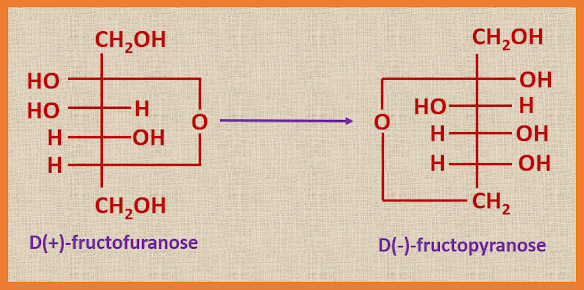
Secondly, hydrolysis of sucrose gives first of all α-D(+)-glucopyranose
and β-D(+)- fructofuranose (this is believed to be dextrorotatory), but the letter is unstable and immediately changes into the stable form, D(-)-fructopyranose (the rotation of (-)-fructose is much greater than that of (+)-glucose).














No comments:
Post a Comment