Peptide Synthesis
Peptide
Peptides are polymers of amino acids containing from 2 to 50 individual units.
The individual amino acids are connected by amide linkages (which are commonly known as peptide linkages) from the amino group of one unit to the carboxyl group of another.
The main structural features of the peptides are that they have a free amino group on one end which is called the N-terminus and a free carboxylic group on the other which is called C-terminus.
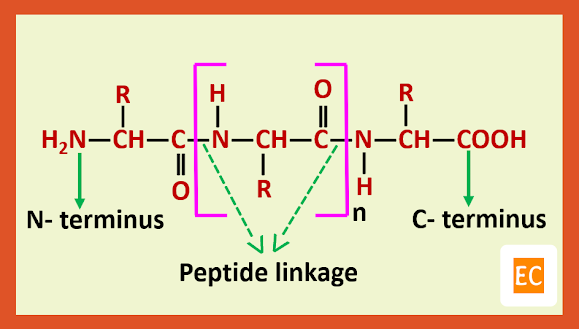 |
They are named from N-terminus to C-terminus through the sequential listing of the names of amino acids. [ Peptides structures are always written with the N-terminal unit on the left and the C-terminal unit on the right]. This is done by replacing the ending -ine by -yl in the names of all amino acids excepting the C-terminus. Quite often the names of the peptides are abbreviated by using three letter abbreviations for amino acids.
H3N+―CH2―CONH―CH2―COO-
Glycylglycine (Gly.Gly)
H3N+―CH2―CONH―CH(CH3)―CONH―CH(CH2OH)―COO-
Glycylalanylserine (Gly.Al.Ser)
Peptide synthesis
We know that peptides are polyamides and can be synthesized by the stepwise condensation in which the amino group of one amino acid is condensed with the carboxylic group of a second amino acid and then so on.
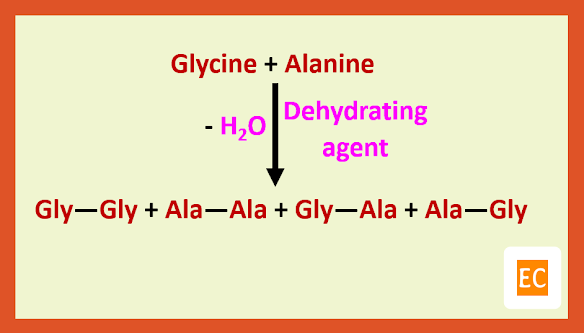
Let us consider the synthesis of a simple dipeptide glycylalanine (Gly-Ala).
Such a direct approach will give four different dipeptides. So, the problem of forming an amide linkage by direct treatment may be removed by the formation of acyl halide.
R―COOH + SOCl2
------> R―CO―Cl
R―CO―Cl + R'―NH2
------> R―CO―NH―R'
But the amino acid can not be converted into an acyl halide, polymerization would result.
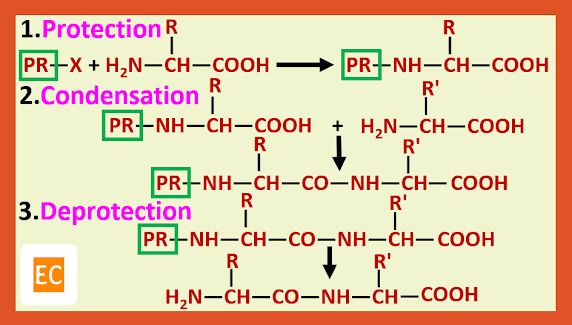
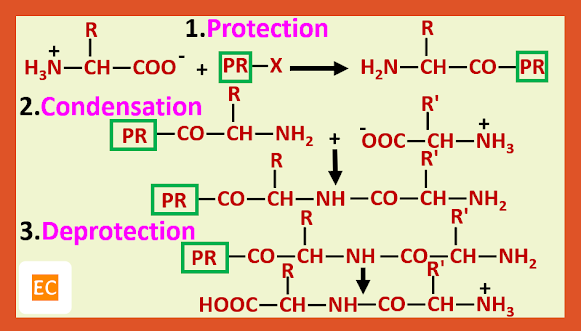
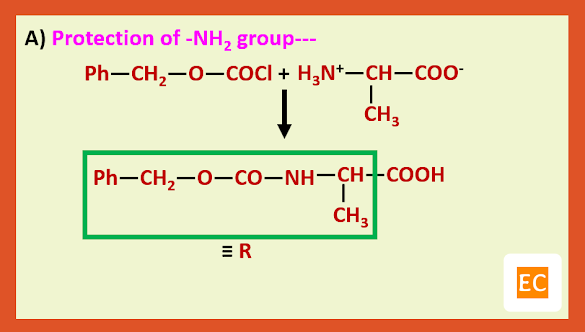
The general method that has been developed to avoid these difficulties involves the use of protecting groups. Protecting groups have been developed for both the amino and carboxy groups.
Peptide synthesis using protecting Amino group:-
Among the many amino protecting groups that have been developed, we shall discuss only two, the benzyloxy carbonyl (carbobenzoxy) and the t-butoxy carbonyl group.
In organic synthesis, generally amino group is protected by acetylation or benzoylation. Neither method is suitable here because hydrolysis of the amide linkage to the protective groups also cleaves the peptide bonds.
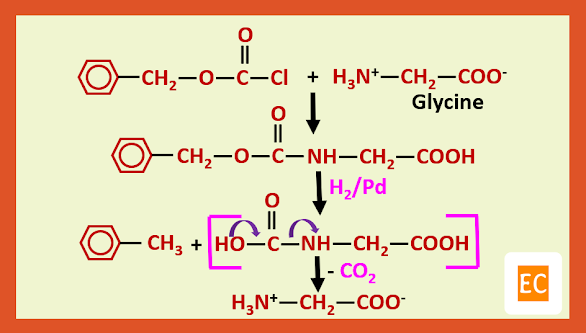
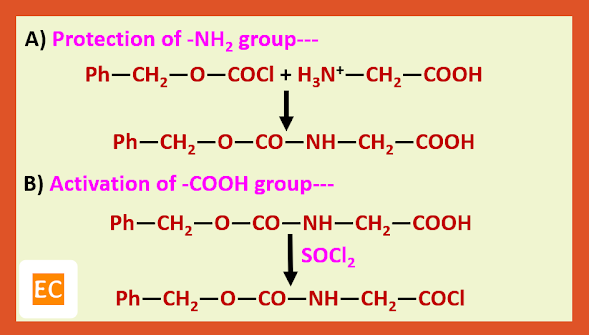
a) Carbobenzoxy protection:---
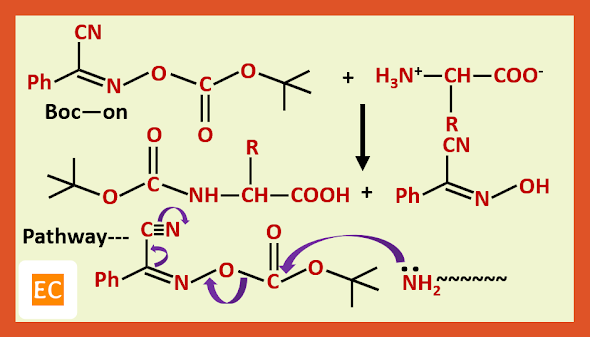
b) The t-butoxy carbonyl group is introduced by treating the amino acid with t-butoxy carbonyl oximino phenyl acetonitrile (BOC-on):---
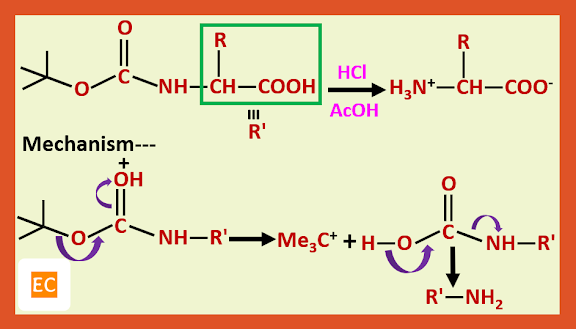
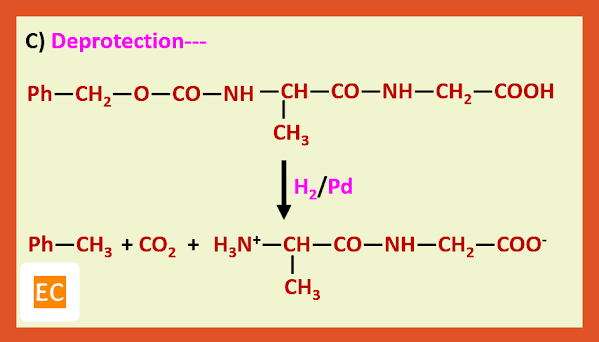
The t-butoxy carbonyl group is removed by treating the protected amino acid or peptide with anhydrous acid, such as CF3COOH or HCl in CH3COOH.
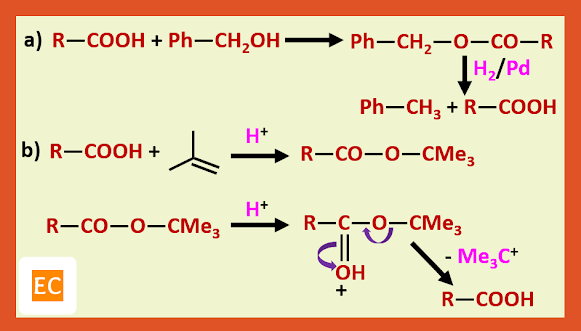
C-Terminus protecting agent:---
Protecting agent is benzyl alcohol:---
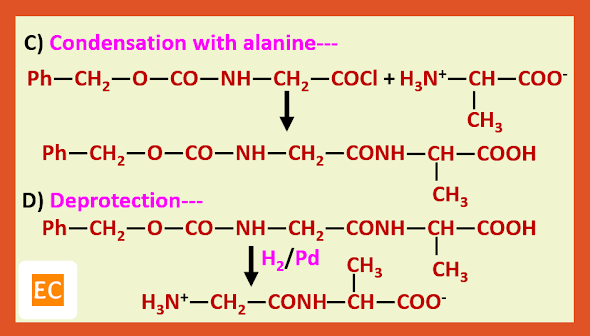
Preparation of glycylalanine:---
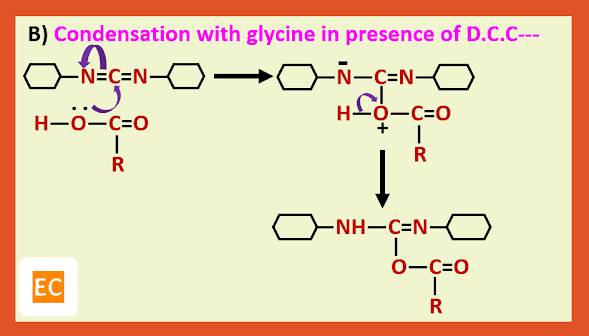
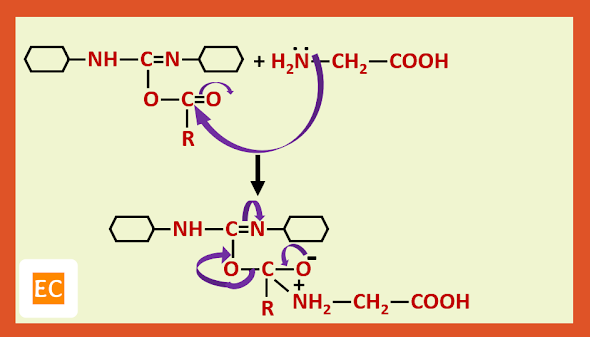
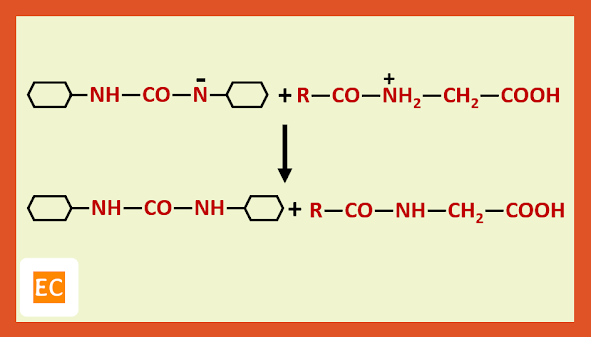
Recently it has been shown that step B can be avoided by treating the protected amino acid with the second molecule of free amino acid in presence of D.C.C (Dicyclohexyl carbodi imide) which is a dehydrating agent of choice for direct conversion of acids into esters and amides.