CARBENE
A reaction in which both the groups or atoms are lost from the same carbon is called an α elimination reaction and results in the formation of carbene.
Carbenes can be defined as neutral divalent carbon intermediates in which a carbon is covalently bonded to two atoms and has two non bonded orbitals containing two electrons between them.
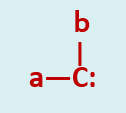 |
| Carbene |
The simplest member of the class is methylene a non-isolable species of molecular formula H2C:
Types of Carbenes
The two nonbonded electrons of a carbene may be either paired or unpaired. If they are unpaired the carbene is said to be in a triplet state, if they are paired then the carbene is called a singlet. One physical property that the singlet carbene is diamagnetic while the triplet is paramagnetic.
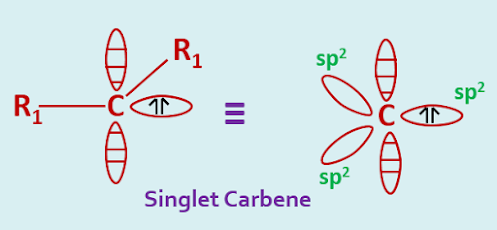
In the singlet state, a carbon atom is presumed to be approximate sp2 hybridization. Two of the three sp2 hybrid orbitals are utilized in forming two covalent bonds whereas the third orbital contains the unshared pair of electrons. The remaining p-orbital remains vacant.
 |
| Singlet Carbene |
The R1—C—R1angle would be expected to be contracted slightly from the normal 1200. The explanation comes from the valence bond electron pair repulsion theory, where l.p—l.p> l.p—b.p> b.p—b.p . Here the inter orbital repulsion will be greatest for the more diffuse lone pair orbital.
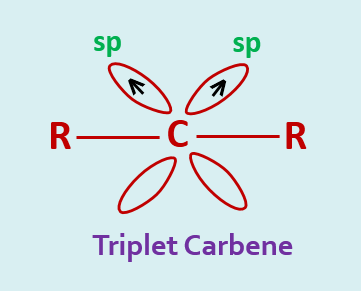
The carbon atom of a triplet carbene is sp hybridized. These two hybrid orbitals are involved in the bond formation with two groups and the remaining two electrons are placed, one each of the two unhybrid p-orbitals. These electrons have parallel spins.
 |
| Triplet Carbene |
Triplet carbene is more stable than the singlet. A triplet carbene is lying at about 8 K.cal/mole lower in energy than the singlet state.
Generation of Carbene
1. Photolysis of diazo compound :
Carbene is usually formed by photolysis of diazo compound when photolysis occurs in the liquid phase singlet carbene generated, but when photolysis occurs in gas phase triplet carbene generated.
 |
| Generation of Carbene by Photolysis |
2. From ketene :
Carbene can be generated from ketene, the reaction occurs in the presence of light in the gas phase.
R2C=C=O ---------> R2C: + CO
3. From alkyl halide :
The three mixed alkyl halide, such as CHF2Cl, CHF2Br, CHF2I undergo concerted elimination to carbenes.
OH- + CHF2Br --------> H2O
+ F2C: + Br-
4. From the reaction of chloroform and base :
When chloroform reacted with a base like K+O-CMe3 dichloro carbene is generated.
HCCl3 + K+O-CMe3
------> Cl3C- + Me3COH + KCl
Cl3C- ----> Cl2C: + Cl-
5. From esters of trichloroacetic acid :
When esters of trichloroacetic acid reacted with a base like MeO- dichloro carbene is generated.
Cl3CCOOEt +MeO- -------> Cl3C-
+ CH3OCOOEt
Cl3C- ----> Cl2C: + Cl-
6. From the reaction of carbon tetrachloride with alkyl lithium :
Butyl lithium and carbon tetrachloride react at low temperature (1000C) through halogen-metal interchange to give lithium trichloromethane. On warming (600C) this lithium salts yield dichloro carbene.
CCl4 + C4H9Li ------>
LiCCl3 + C4H9Cl
LiCCl3 -------> Cl2C: + LiCl
Reactions of Carbene
1.Cycloaddition reaction :
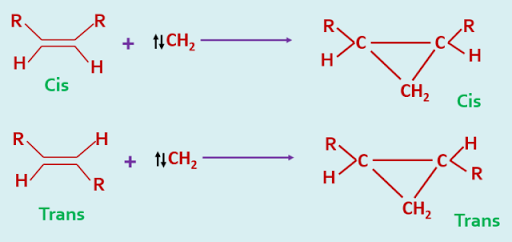
Singlet carbenes add to alkenes in a stereospecific manner i.e stereochemistry of the alkene is retained in the cyclopropane.
 |
| Addition of Singlet Carbene |
In contrast, the addition of triplet carbenes to alkenes takes place with non stereospecificity.
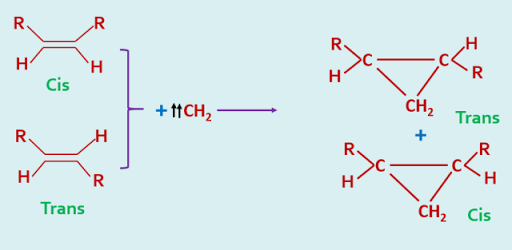 |
| Addition of Triplet Carbene |
The stereochemistry of these cycloaddition is so specific that it may be used as a diagnostic test for the identification of singlet and triplet carbenes.
The difference in behaviour between these two electronic states of a carbene has been explained in the following way. The addition of a singlet carbene to an alkene is a concerted process as there is no spin restriction on the simultaneous formation of two new sigma bonds of the cyclopropane, and hence it is a stereospecific process.
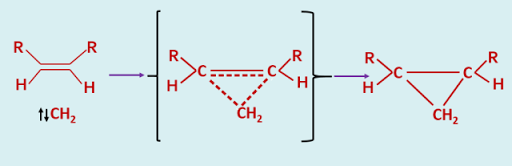 |
| Addition of Singlet Carbene - a concerted process |
In the case of triplet carbene, a cyclic transition state is not formed, the addition occurring stepwise as a radical fashion. This is represented as follows, the arrows indicating the direction of spin of each unpaired electron, and the assumption is made that the rotation about the single bond is more rapid than spin inversion.
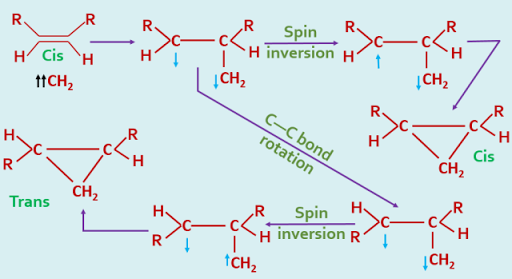 |
| Addition of Triplet Carbene - stepwise process |
2. Insertion reaction :
Frequently carbenes can be inserted into a C—H bond.
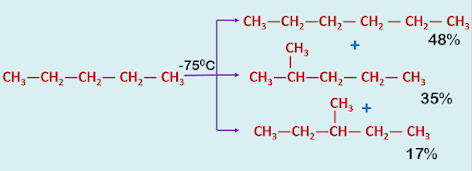 |
| Insertion Reaction of Carbene |
The mechanism for insertion are recognized, it may be one step process or it may be two steps process.
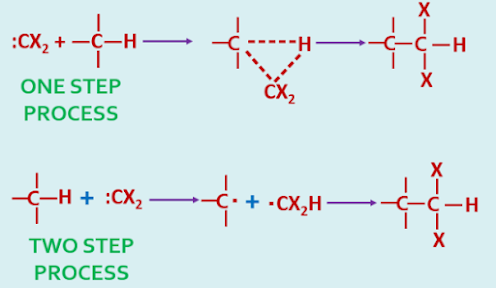 |
| Mechanism of Insertion Reaction of Carbene |
3.Simon-smith reaction :
Difficulty for the preparation of cyclopropane derivative using :CH2 and the solution is by using Simons-Smith reagent.
The addition of methylene, derived from diazomethane, ketene etc, to olifins is synthetically inefficient since insertion is a competing reaction.
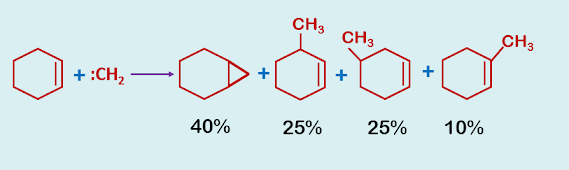 |
| Reaction of cyclohexene with carbene |
When an alkene is treated with methylene diiodide CH2I2,in presence of Zn-Cu couple we get a cyclopropane derivative.
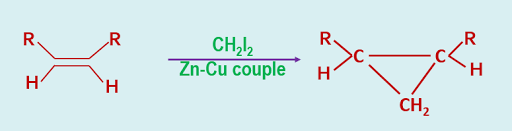 |
| Simon-Smith Reaction of Carbene |
This is known as Simon-Smith reaction.











No comments:
Post a Comment